Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Given that this is a cohort study, the relative risk (RR) should have been calculated instead of the odds ratio Odds ratios frequently generate larger differences between exposed and nonexposed groups (especially when dealing with nonrare events), therefore overestimating the observed effect (4)A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical
How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk-When used for cohort studies and randomized clinical trials, the odds ratio is often incorrectly interpreted as the risk ratio; Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology
The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups The interactive feature below allows you to simultaneously compute both the risk ratio and the odds ratio in a hypothetical cohort study In general, the odds ratio will be close in value to the risk ratio when the outcome of interest is rare, but Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32
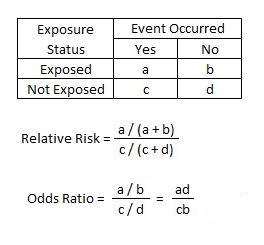
Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trials Consider again the data in the table below from the randomized trial assessing the effectiveness of a newly developed pain reliever as compared to the standard of care
Nonexposed group, "OR" is an odds ratio from a logistic regression equation, and "RR" is an estimated relative risk Most researchers apply this formula to the adjusted odds ratio to estimate an adjusted relative risk Using the formula in this manner is incorrect and will produce a biased estimate when confounding is presentAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% =The quote surely just means to say that the odds ratio is a relative risk measure rather than an estimate of the relative risk, which as already point out is only approximately the case in cohort studies/randomized trials for very low proportions By relative risk measure I mean something that is given relative to some comparison group in a way that the absolute difference depends on the



Www Nature Com Articles Pcrj006 Pdf Origin Ppub



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk; MantelHaenszel methods for stratified summaries of odds ratios have been extended to summarize risk ratios using matchedpair cohort data (1, 12– 16) The estimator of the risk ratio from the matched pairs reduces to the crude risk ratio described above Using the notation from table 1, this estimator is (A B)/(A C) The risk ratio, also referred to as the relative risk, is calculated as the ratio of the risk of the outcome in these two groups In this article, we illustrate, by means of two empirical examples, that use of odds ratios in cohort studies and




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Both the relative risk and odds ratio are relevant in retrospective cohort studies, but only the odds ratio can be used in casecontrol studies Although most casecontrol studies are retrospective, they can also be prospective when the researcher still enrolls participants based on the occurrence of a disease as new cases occurAbstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Estimating Risk
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsOdds ratios and risk ratios •How do you interpret the relative risk?Converting Odds Ratio to Relative Risk in Cohort Studies with Partial Data Information Zhu Wang Connecticut Children's Medical Center Abstract In medical and epidemiological studies, the odds ratio is a commonly applied measure to approximate the relative risk or risk ratio in cohort studies It is well known tha such




Relative And Absolute Risk Osmosis




Gordis 12 Biostatistics Risk Relative Risk Odds Ratio Flashcards Quizlet
ERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi for Other O does not have an R (cOhort), which means the other group does not have the risk factor Compare the two to see who gets the disease How to remember that case control studies measure odds ratio and cohort studies measure relative risk You take surgical "cases" to the "OR" (Operating room) Case control study Odds Ratio cohoRRRRRRtThe odds ratio then provides an overestimation of the risk ratio, especially when the outcome is frequent The use of logistic regression to adjust for confounding is one of the reasons that odds ratios are presented



Hierarchy Of Study Design Descriptive Studies Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study − The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study 33 When Is Odds Ratio a Good Estimate of Relative Risk? It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube
Hi, Been reading through a research paper that used a prospective cohort study, but in the results table for measures of association, the odds ratio was used instead of relative risk This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regression When the incidence of an outcome is low (In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospective studies, attributable risk can not be calculated




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedOdds ratio = odds of exposure (cases) = ad odds of exposure (controls) bc Cohort studies The relative risk is the measure of association for a cohort study It tells us how much more likely (or less likely) it is for people exposed to a factor to develop a disease compared to people The odds ratio (OR) or the ratio of odds of exposure is thus given by a/cb/d (or ad/bc) The odds ratio is generally a good estimate of the relative risk The terms odds ratio and relative risk are in fact interchangeable when used in casecontrol studies Population and hospitalbased casecontrols studies




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Odds of the disease in men Odds=Risk of disease in men/risk of no disease in men= (140/0)/(60/0)=07The risk of getting the disease in males is 31 times the risk of getting the disease in females •What is the odds ratio for the disease among men as opposed to women? 2) Cohort studies will have information about persontime at risk, and so the desired outcomes are often incidence rates, population attributable risk, or risk ratios The odds ratio estimate for rare outcomes will approximately estimate the risk ratio in this design, but it makes more sense to compute the risk ratio directly



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology



Marg Innovera
Davies et al (1) state that the odds ratio is a common measure in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trails Unfortunately, this first sentence of their article is not correct For different study designs, OR should only be used as a measure of effect size when RR can not be estimated directly9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsThe prevalence odds ratio The prevalence odds ratio (POR) is calculated in the same manner as the odds ratio The prevalence ratio The prevalence ratio (PR) is analogous to the risk ratio (RR) of cohort studies The denominators for both ratios are fixed populations – fixed at the start of the study in the case of a cohort study, and fixed at




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
Risk Ratio 31 • Can also be called Relative Risk or RR Exposure odds ratio • Similar to risk ratio from cohort study • PR= Prevalence of disease in exposed group/ Prevalence of disease in unexposed group OR Relative risks and odds ratios are widely reported in the medical literature, but can be very difficult to understand We sought to further clarify these important indices Methods We illustrated both relative risks and odds ratios using bar charts, then looked at the types of study for which each statistic is suitedความเสี่ยงสมพันธั์ (Relative risk) risk ratio relative risk เท่ากับ ค่าอัตราส่วนของ p1/p2 Cohort Study risk ratio = 12/22 =55;




Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
95%ci ของ rr = 32, 95 2 2 1 1 /2 (1 )100%confidence interval rr log 1 1 1 n p p p z p pWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2
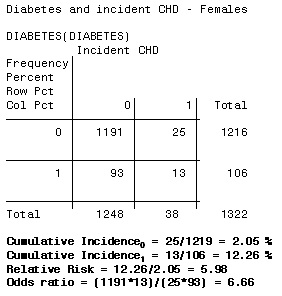



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
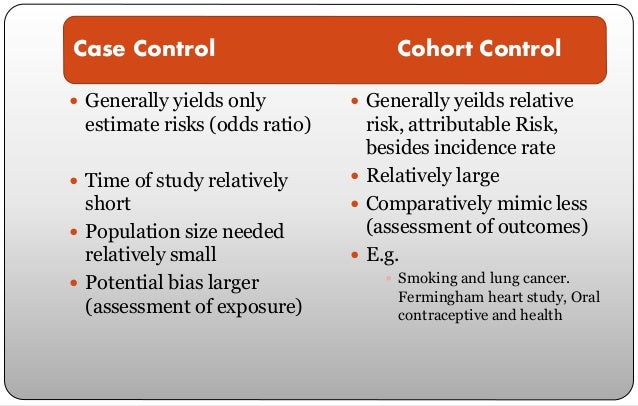



Cohort And Case Con Revised




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Article



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com




Comparison Of Three Methods For Estimating Relative Risk In A Cohort Download Table




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Http Osctr Ouhsc Edu Sites Default Files 02 Module7partinotes Pdf
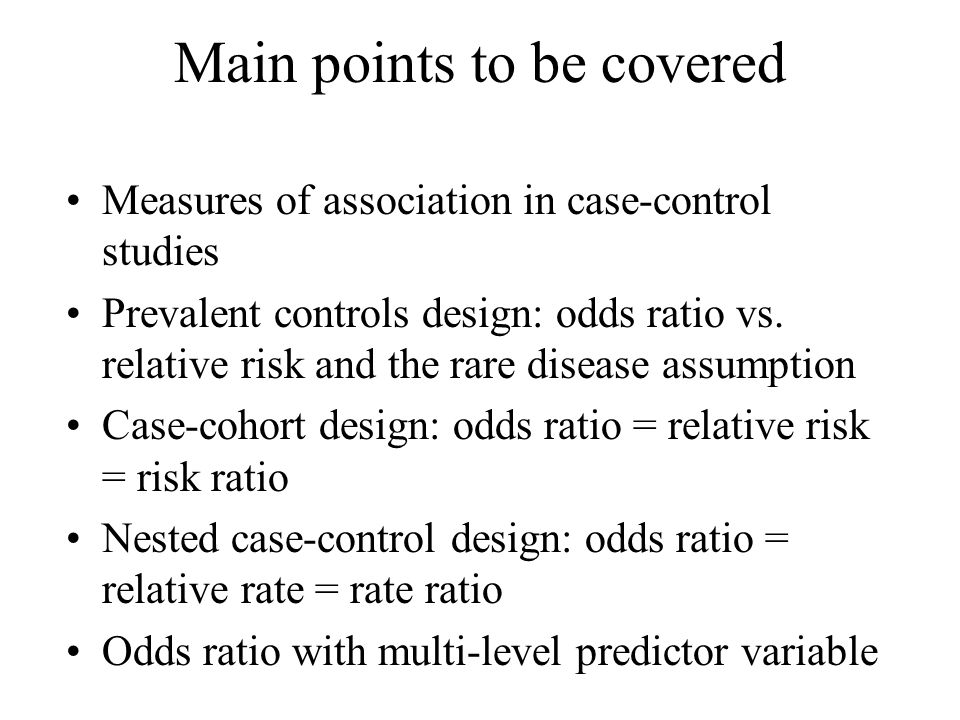



Main Points To Be Covered Measures Of Association In Case Control Studies Prevalent Controls Design Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk And The Rare Disease Ppt Download




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Relative Risk Article




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc
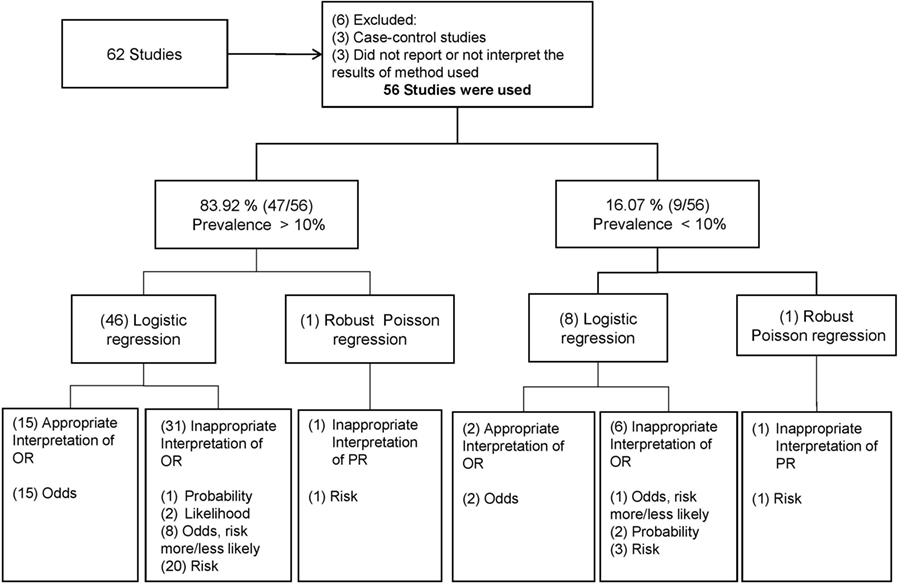



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
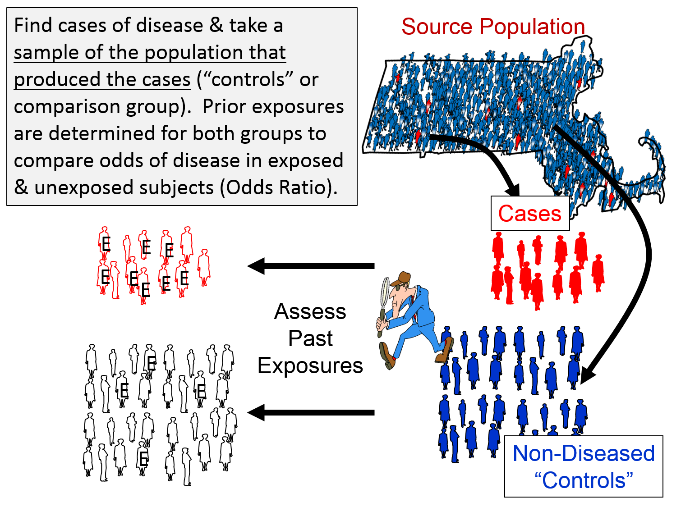



A Nested Case Control Study




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
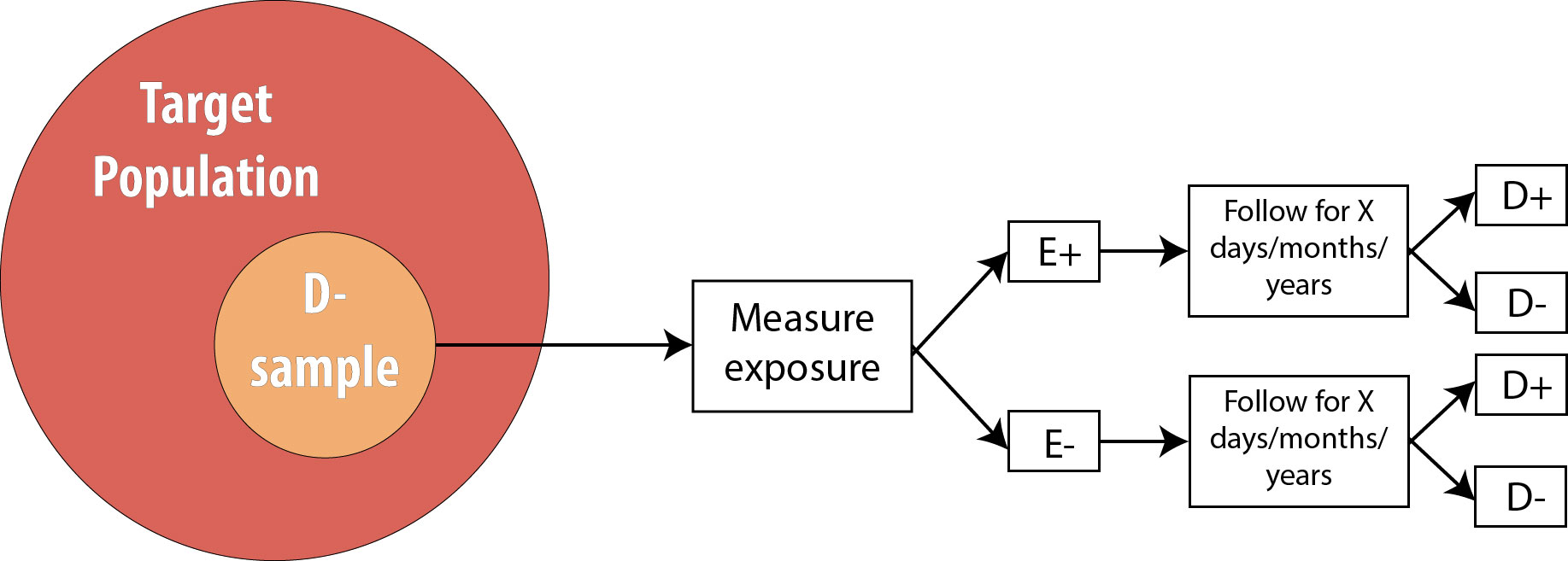



Introduction To 2 X 2 Tables Epidemiologic Study Design And Measures Of Association Foundations Of Epidemiology




Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram



Epidemiology Amboss




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney
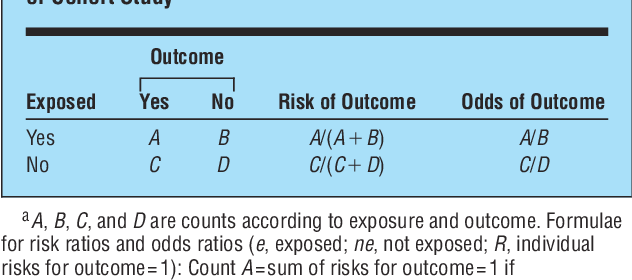



Table 1 From The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Relative Risk Wikipedia
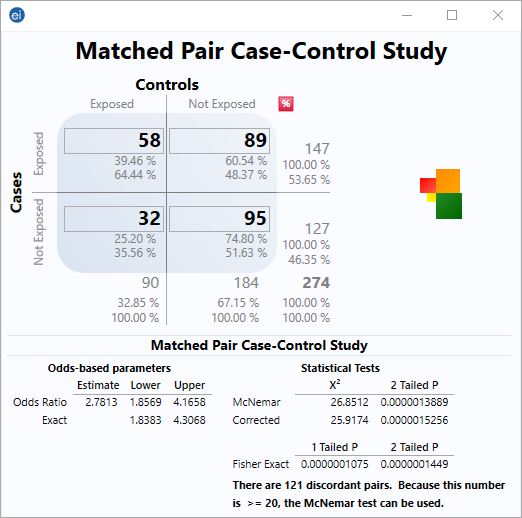



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc



Escholarship Umassmed Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1013 Context Liberia Peer




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy On Vimeo
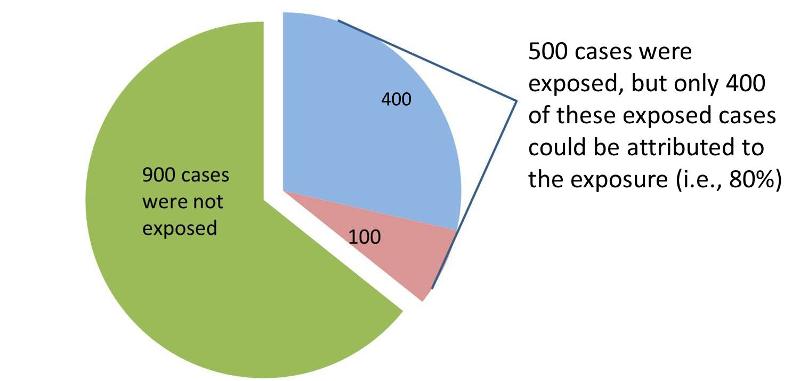



Measures Of Association
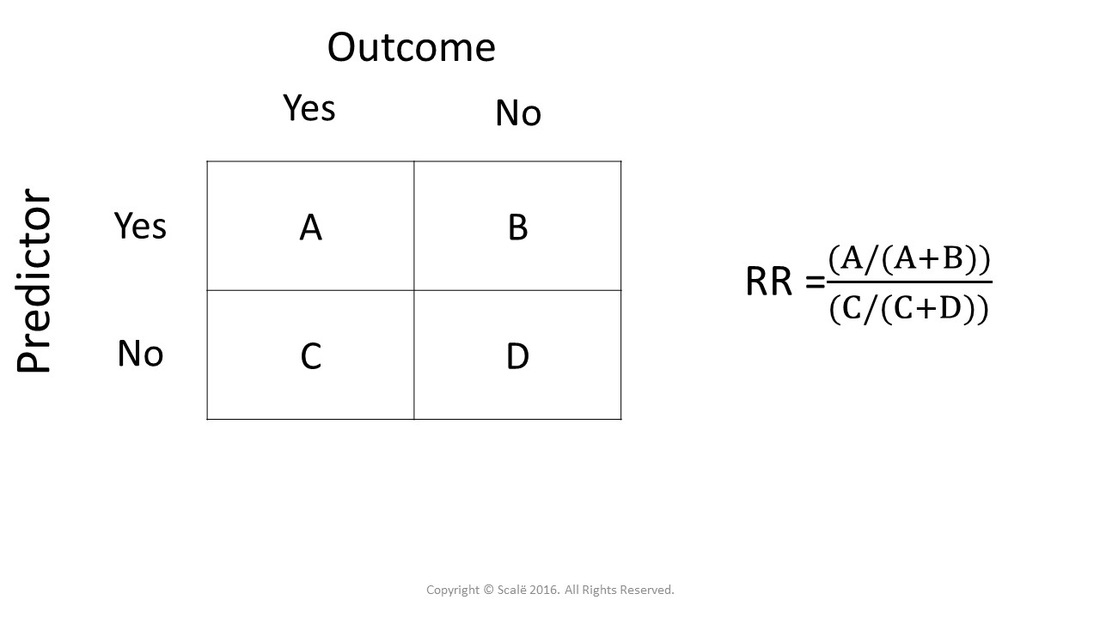



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Measures Of Association Blood Pressure Odds Ratio




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
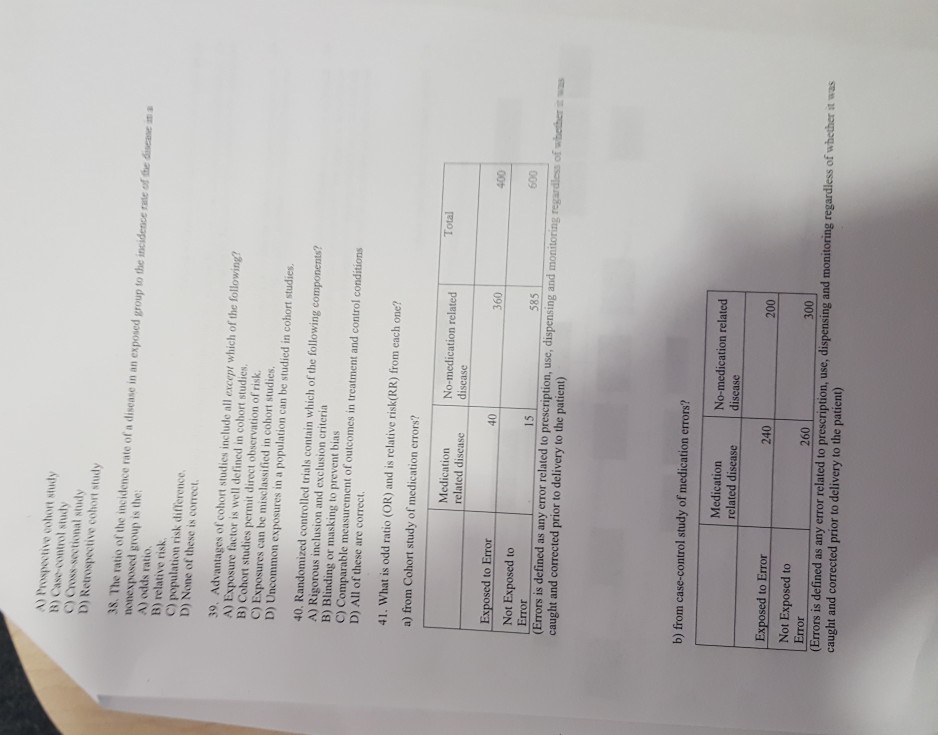



A Prospective Cohort Study B Case Control Study C Chegg Com




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice



Support Sas Com Resources Papers Proceedings11 345 11 Pdf




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
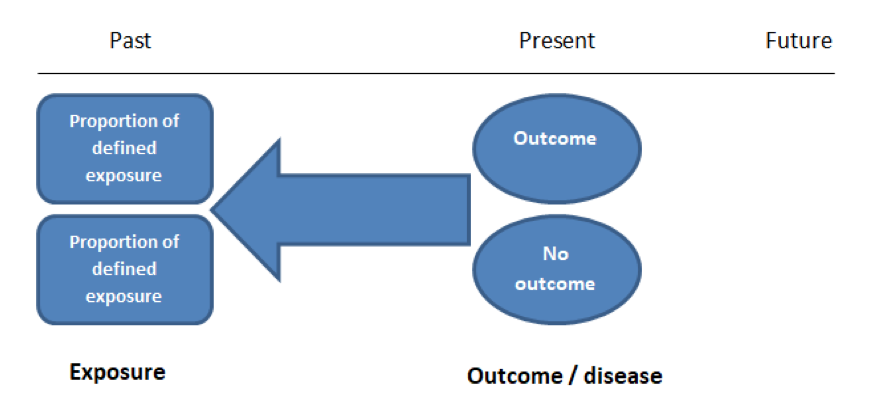



Case Control And Cohort Studies A Brief Overview Students 4 Best Evidence




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Q Tbn And9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau




Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Chegg Com




Figure 2 From Secondhand Smoke Exposure And Risk Of Lung Cancer In Japan A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Epidemiologic Studies Semantic Scholar



Content




Relative And Atribute Risk




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




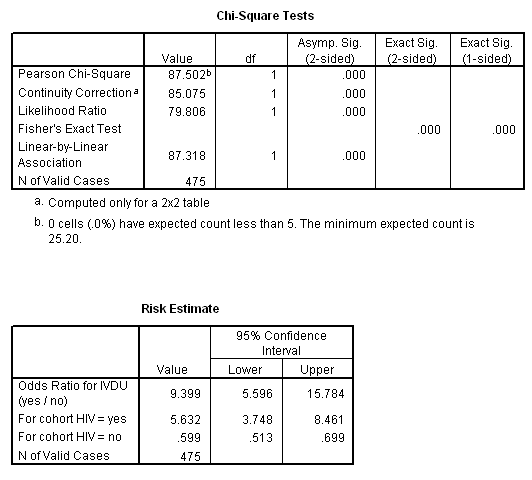
How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
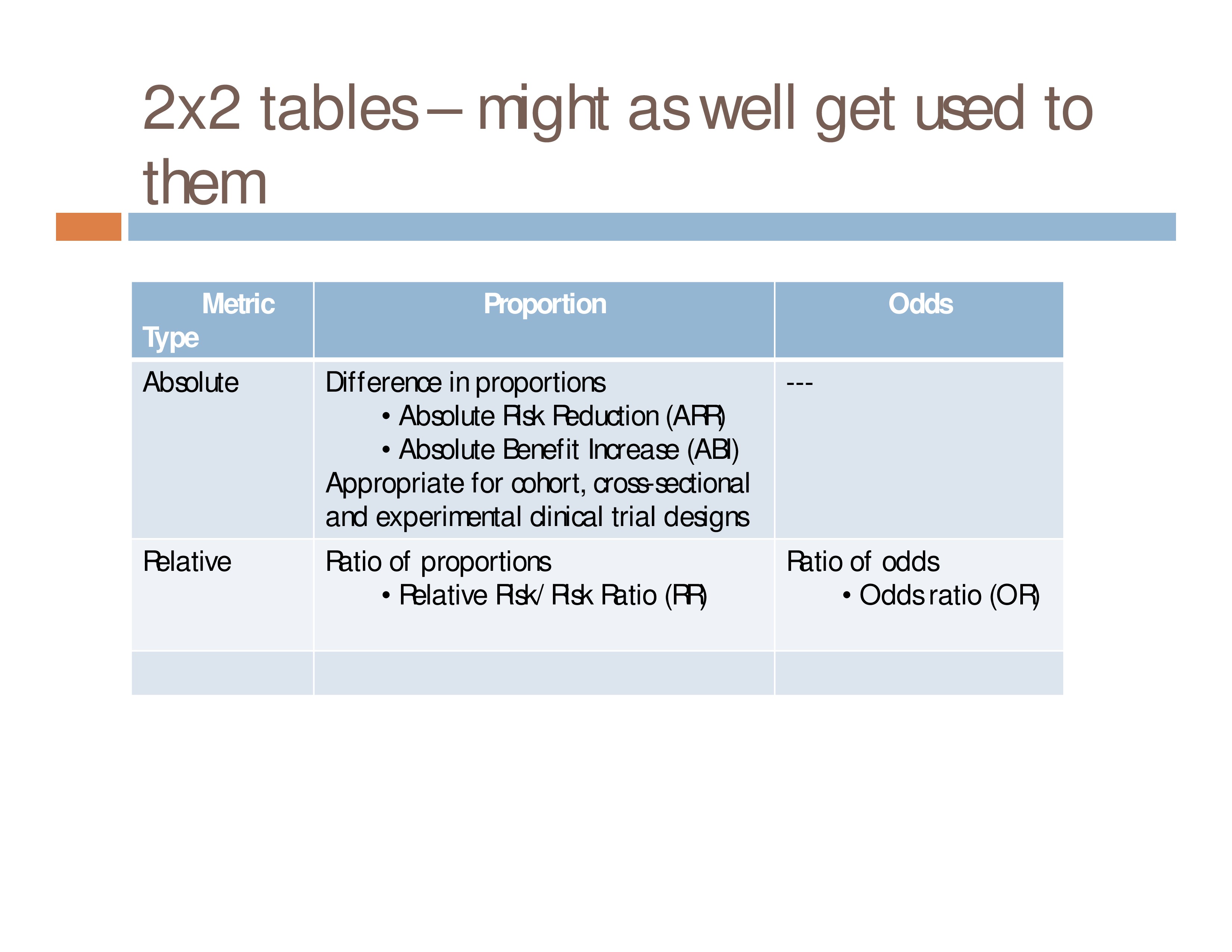



Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy



Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿